Title: A Comprehensive Guide to Tuberculosis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Dietary Considerations, Treatment, and the Role of Exercise:
Introduction:
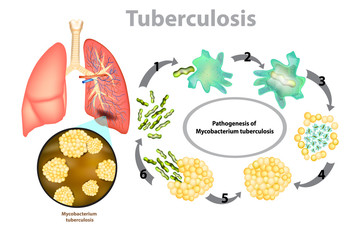
Tuberculosis (TB) is a potentially severe infectious disease that predominantly affects the lungs but can impact other parts of the body. It's caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB spreads from one person to another through tiny droplets released into the air via coughs and sneezes. Understanding the different types of TB, their symptoms, causes, dietary considerations, and treatment options, as well as the role of exercise in managing the disease, can be instrumental in managing and overcoming this ailment.
Types of Tuberculosis:
Tuberculosis can be classified into two main types: latent TB and active TB.
Latent TB:
Latent TB infection (LTBI) implies that an individual is infected with the TB bacteria but does not show symptoms as the bacteria remain inactive in the body. People with LTBI do not feel sick, cannot spread the bacteria to others, but they may develop TB disease if they do not receive treatment.
Active TB:
Active TB disease occurs when the bacteria become active in the body, causing symptoms. Unlike LTBI, this form of TB can be infectious, meaning it can spread from person to person.
Further Classification:
Tuberculosis can also be classified based on the organs it affects, such as:
Pulmonary TB: This form affects the lungs and is the most common form of the disease. It's highly infectious as the bacteria can be spread through the air when the affected individual coughs or sneezes.
Extrapulmonary TB: This form affects organs outside the lungs, such as the kidney, spine, brain, or lymph nodes. It is less likely to be contagious unless it affects the larynx (voice box).
Causes and Symptoms:
The primary cause of TB is the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It spreads through tiny airborne droplets when a person with pulmonary or laryngeal TB sneezes, coughs, speaks, or sings.
Common symptoms include persistent cough that lasts three or more weeks, chest pain, coughing up blood, fatigue, weight loss, fever, night sweats, chills, and loss of appetite. Symptoms may vary for extrapulmonary TB depending on the affected organ.
Dietary Considerations:
Foods to Eat:
Maintaining a balanced diet is critical when dealing with TB. A diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals is recommended. Consuming fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants, such as berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens, can help boost the immune system. Protein-rich foods like lean meats, eggs, dairy, and legumes support tissue repair and regeneration. Carbohydrates provide energy, so whole grains and starchy vegetables should be included in the diet.
Foods to Avoid:
People with TB should avoid alcohol, as it can interact with TB medications and cause liver damage. Also, excessive intake of coffee and other caffeinated beverages should be minimized as they can interfere with the body's ability to absorb calcium. Foods with high sugar content and processed foods should be limited, as they can lead to unhealthy weight gain and other health issues.
Treatment:
TB is treatable and curable, primarily through the use of antibiotics. Treatment usually lasts for at least six months and may extend depending upon the type and severity of the disease. The most common drugs used include Isoniazid, Rifampin, Ethambutol, and Pyrazinamide. Adherence to the prescribed drug regimen is crucial to cure the disease and prevent the development of drug-resistant TB.
The Role of Exercise:
Regular exercise can be beneficial for people with TB by strengthening their immune system, improving their appetite, and reducing stress levels. Activities such as walking, yoga, and gentle strength training can help improve overall health and well-being. However, it's crucial to start slow and gradually increase intensity based on individual capacity and comfort.
Conclusion:
Tuberculosis is a serious disease, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, it can be managed effectively. Understanding the different types, causes, and symptoms of TB, along with making dietary adjustments and incorporating regular exercise, can significantly contribute to recovery and quality of life during and after treatment. It's essential to remember that treatment adherence is key to preventing the spread of the disease and emergence of drug-resistant forms of TB. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.
- Can you define what Tuberculosis (TB) is and how it affects the human body?
- What causes Tuberculosis, and how is it transmitted from person to person?
- What are the typical symptoms of Tuberculosis, and how is it diagnosed?
- What treatment options are available for Tuberculosis, and how effective are they?
- Can you explain the global impact of Tuberculosis, including its prevalence and the populations most affected by it?








No comments
Please do not enter spam link in the comment box